
The
Lafforgue's Electrostatic Pressure Experiment
by Jean-Louis
Naudin
created on January
20, 2002 - JLN Labs - Last
update January 31, 2002
All
informations in this page are published free and are intended for
private/educational purposes and not for commercial applications
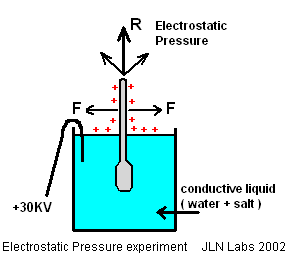
On January 23, 2002, I have tested successfully the Jean-Claude Lafforgue's basic experiment about the Electrostatic Pressure. An asymmetrical electrostatic pressure is the main principle used in his patent for producing a thrust Vs external referential ( the Universe ). Lafforgue has called this the " Action Force " or the " Expansion Force ". The setup of this electrostatic pressure experiment is fully described in his patent FR2651388 page 35. Some translations of the Lafforgue's patent can be found here.
This experiment is well known in high schools ( i.e : See " Electrostatique, Electrocinétique " by Maurice Ravaille - Collection de Sciences Physiques dirigée par Marcel Peschard Edition Baillère, page 125 ).
Tested apparatus description :
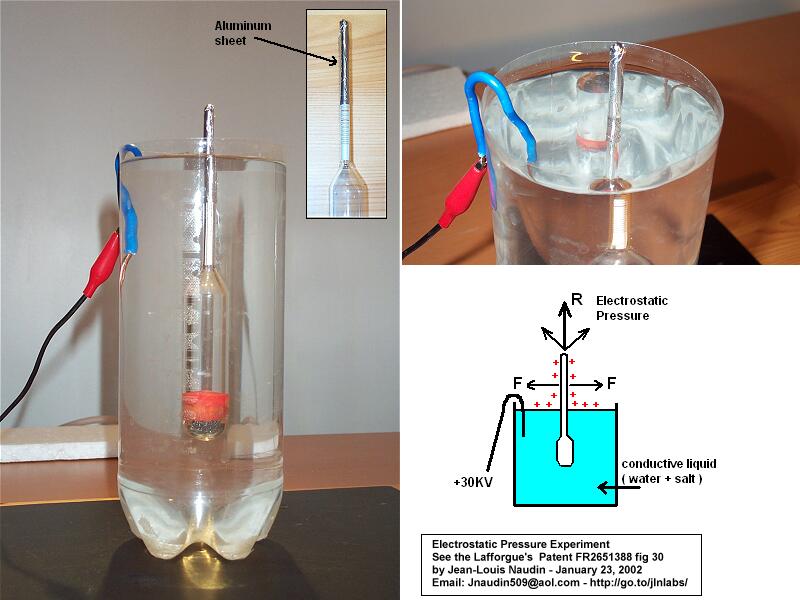
I have used a glass aerometer ( hydrometer ) commonly used for measuring the liquid density. The upper part of the glass aerometer has been covered with an aluminum sheet on about 50mm length, see the photo below :
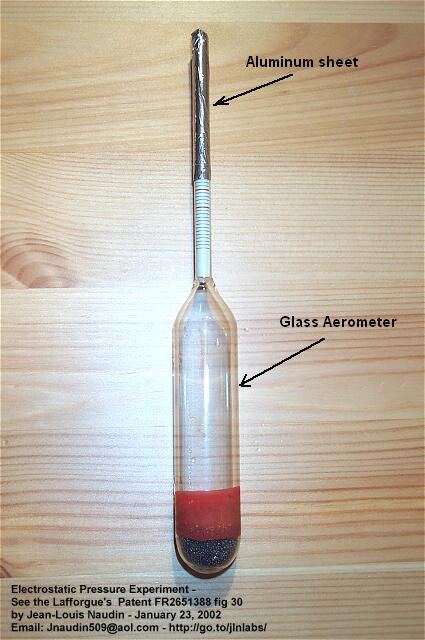

Then the areometer ( hydrometer ) is placed in a plastic vessel filled with a mixture of 1.25 Liter of water and 1 coffee spoon of salt. The bottom end of the aluminum shape must be just about 15 mm below the surface of the salt water. A copper wire is immersed in the water and connected to a +30 KV DC power supply.
TESTS RESULTS ( 01-23-02 ) :
When High Voltage ( +30 KV DC ) is switched on the aerometer ( hydrometer ) goes upward because the resulting electrostatic pressure on all the conductive surface of the aerometer becomes asymmetrical ( see the photo below )


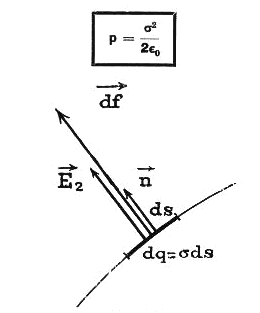
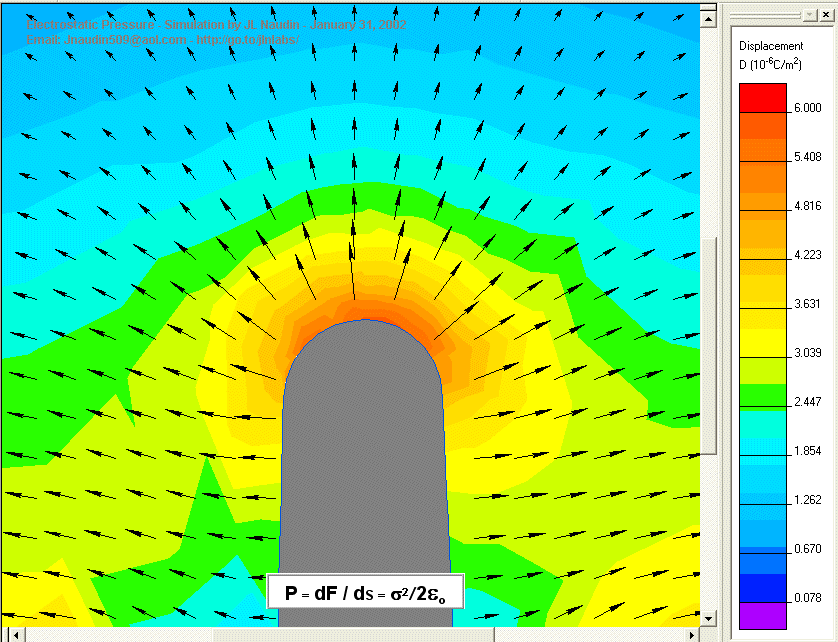
The electrostatic pressure is independant of the voltage polarity,
perpendicular to the conductive armature surface
and always towards to the
outside of the shape
| P = dF / dS = s2/2eo |
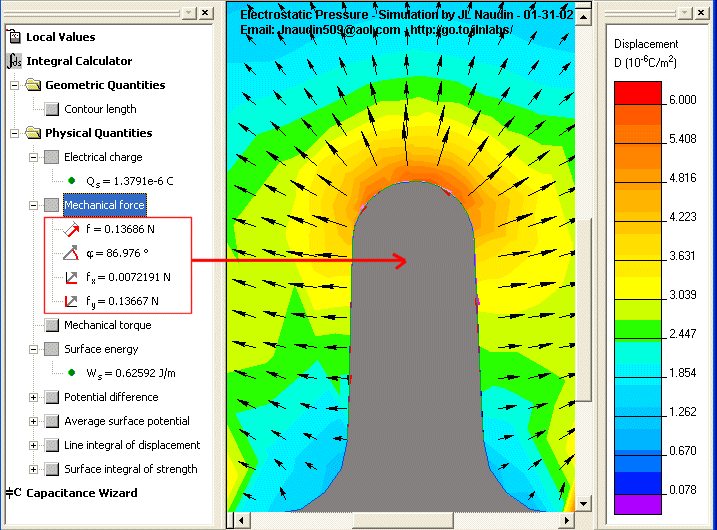
I encourage anyone who wants to conduct some researches in this domain, to study this patent very carefully....
|
|||||||||||||||
See the video of Lafforgue's Electrostatic Pressure experiment
To see the videos, the free
downloadable RealPlayer is required ![]()
Click on the picture above to see the video ( 262 Kb )
Some documents references :
 FR Patent N°2651388 "Isolated systems self-propelled by
electrostatic forces"
by Lafforgue Jean-Claude - March 1, 1991
FR Patent N°2651388 "Isolated systems self-propelled by
electrostatic forces"
by Lafforgue Jean-Claude - March 1, 1991See also :
 Asymmetrical
Electrostatic Pressure on a charged body
Asymmetrical
Electrostatic Pressure on a charged body
 The LPT v1.0 pulsed
tests without leakage current
The LPT v1.0 pulsed
tests without leakage current
![]() Email : JNaudin509@aol.com
Email : JNaudin509@aol.com
Return to the LFPT home page